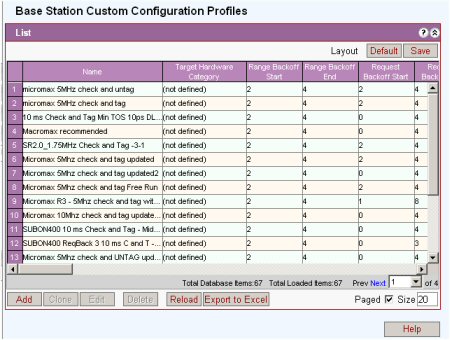
BS TRx Custom Configuration package is defined for the specific target hardware category. The BS TRx Channels of different categories will not be able to have wrong profile assigned.
The exception is category (not defined), which is maintained for backwards compatibility purposes with older versions of Netspan databases.
Profiles of (not defined) category cannot be used for MicroMAX.

See Add/Edit Custom Configuration below
See Action Buttons
Different configurations are displayed for HiperMAX, HiperMAX-micro, MacroMAX and MicroMAX
The use of hardware specific profiles means that only those items relevant to the specific hardware are displayed in the window.
HiperMAX, HiperMAX-micro, MacroMAX
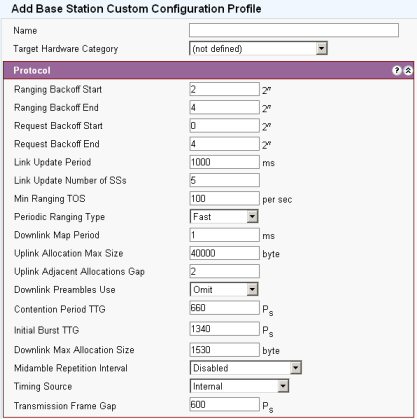
The ranging process establishes an appropriate connection for the SS
Ranging Backoff Start: Initial backoff window size for initial ranging contention, expressed 2 to the power n. Values of n range from 0 to 15
Ranging Backoff End: Final backoff window size for initial ranging contention, expressed 2 to the power n. Values of n range from 0 to 15
Request Backoff Start: Initial backoff window size for contention BW requests, expressed 2 to the power n. Values of n range from 0 to 15
Request Backoff End: Final backoff window size for contention BW requests, expressed 2 to the power n. Values of n range from 0 to 15
Link Update Period: Period between fast power control messages. Unit = ms.
Link Update # SS: Sets the number of SSs that can be concurrently updated.
Min Ranging TOS: The number of transmission opportunities to contend for bandwidth per second
Periodic Ranging Type: 0=regular 1=Fast. Always set to 1
Downlink Map Period: The maximum interval that the BS TRx will allow between the transmission of DL Maps.
Uplink Allocation Max Size: The upper limit in bytes of any single allocation that may be granted to an SS in the uplink
Uplink Adjacent Allocations Gap: This sets the gap to be placed between two consecutive bursts from the same SS. Default = 2 symbols
Downlink Preambles Use: Preambles are bursts used to allow the SS to re-synchronize. Enable in fading environments
Contention Period: The turnaround gap between the last DL burst and the next uplink contention slot
Initial Burst TTG: Gap between the end of the initial burst and the start of uplink processing.
Downlink Max Allocation Size: The upper limit in bytes of any single allocation that may be granted to an SS in the dowmlink
Midamble Repetition Interval: A preamble precedes each frame and this sets the number of bytes for a midamble 0(disable),4,8or 16
Timing Source: Used for systems that have GPS timing sources implemented
Transmission Frame Gap: Interval between transmission frame
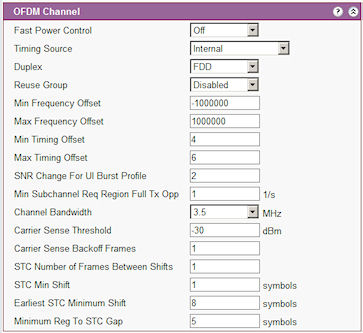
Fast Power Control: Set 'on' to enable Fast Power Control. This allows the BS TRx to adjust the power levels of multiple subscribers simultaneously
Timing Source: Options are 'GPS Suppress', 'GPS No Suppress' or 'Internal'. This sets the response of the BS TRx to loss of synchronisation from the GPS. 'GPS Suppress' will disable the BS TRx from running without synchronisation. 'GPS No Suppress' allows the BS TRx to continue to run on its own internal timing source. 'Internal' forces the BS TRx to run on its own internal timing source.
Duplex: Select FDD or TDD
Reuse Group: When two adjacent sectors share the same channel different reuse groups are set for each sector. SSs that can see both sectors will only sign on to one sector. Select a different group for each sector.
Min Frequency Offset: Not Implemented
Max Frequency Offset: Not implemented
Max/Min Timing Offset: During ranging the timing is adjusted by the BS TRx. These fields set the maximum / minimum offset limits that the BS TRx is permitted to use. The range is -5 to +15 Recommended min=4 max=6
SNR Change For UI Burst Profile: Sets the change in SNR required to initiate evaluation of uplink modulation. Typically 0.5dB.
Min Subchannel Req Region Full Tx Opp. Rate of subchannel bandwidth opportunities 1/s. Not supported
Channel Bandwidth: Select the required channel bandwidth.
Carrier Sense Threshold dBm
Carrier Sense Backoff Frames
STC Number of Frames Between Shifts
STC Min Shift symbols
Earliest STC Minimum Shift symbols
Minimum Reg To STC Gap symbols
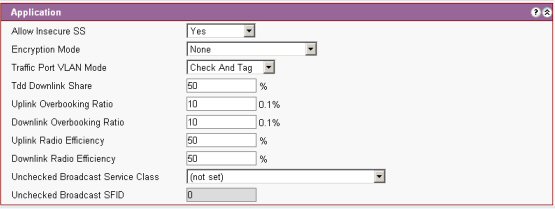
Allow Insecure SS: Select 'Yes' to enable
Encryption mode: Select required encryption mode.
Traffic Port VLAN Mode. Select Check and Tag or Untagged. See VLAN Scenarios
TDD Downlink Share: Sets Percentage of frame used for the DL. Does not include overheads and uplink.
Downlink/Uplink Overbooking Ratio: The percentage CIR over booking allowed on the shelf. Individual channel overbooking is controlled by the QOS.
Downlink /Uplink Radio Efficiency: Sets percentage of link used for traffic. This setting effects how much CIR can be committed CIR
Unchecked Broadcast Service Class: Select Service class for Raw VLAN
Unchecked Broadcast SFID: set by VLAN
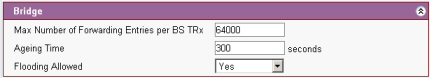
Max Number of Forwarding Entries per BS TRx : Maximum number of entries in routing table for the BS TRx.
Ageing Time: Time to live for routing table
Flooding Allowed: When an unknown packet arrives at BS TRx it is broadcast to all the SSs on that BS TRx if flooding allowed is set to 'yes'. If flooding allowed is set to 'no' then the packet is discarded.
The use of hardware specific profiles means that only those items relevant to the specific hardware are displayed in the window.
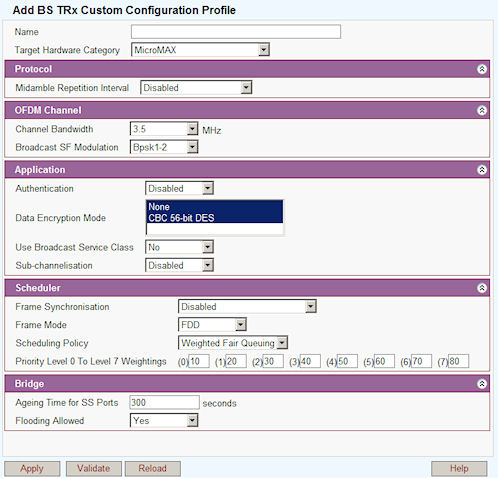
Name: User defined Text .
Target Hardware Category: Select MicroMAX from list.
Midamble Reception Interval: Sets the number of symbols as the interval for reading packet header information.
Channel Bandwidth: Select the required channel bandwidth from 1.75, 2.5, 2.75, 3, 3.5, 5, 7, or 10 MHz.
Broadcast SF Modulation: Select modulation type.
Authentication: Select from Disabled/ Enabled.
Data Encryption Mode: Select from None, CBC, 56-bit DES.
Use Broadcast Service Class: Select No/ Yes.
Sub-channelisation: Select Enable or Disable.
GPS Synchronisation: Select from Disabled, Send Trap And Stop, Send Trap And Continue.
Frame Synchronisation:
Frame Mode: Select from TDD/ FDD.
Scheduling Policy:
Strict: Equal priorities FIFO.
Weighted Fair Queueing: Service shares for each priority are set using weightings set into the boxes. Provides consistent response time to heavy and light network users alike without adding excessive bandwidth. A flow based queuing algorithm that creates bit-wise fairness by allowing each queue to be serviced fairly in terms of byte count. For example, if queue 1 has 100-byte packets and queue 2 has 50-byte packets, the WFQ algorithm will take two packets from queue 2 for every one packet from queue 1. This makes service fair for each queue: 100 bytes each time the queue is serviced.
Ageing time for SS Ports: Time to live for routing table.
Flooding Allowed: When an unknown packet arrives at BS TRx it is broadcast to all the SSs on that BS TRx if flooding allowed is set to 'yes'. If flooding allowed is set to 'no' then the packet is discarded.
See Action Buttons